For the first time in many years, England is recording an exceeding level of gonorrhoea and syphilis sexually transmitted infections, sequel to a dip during Covid years, according to figures.
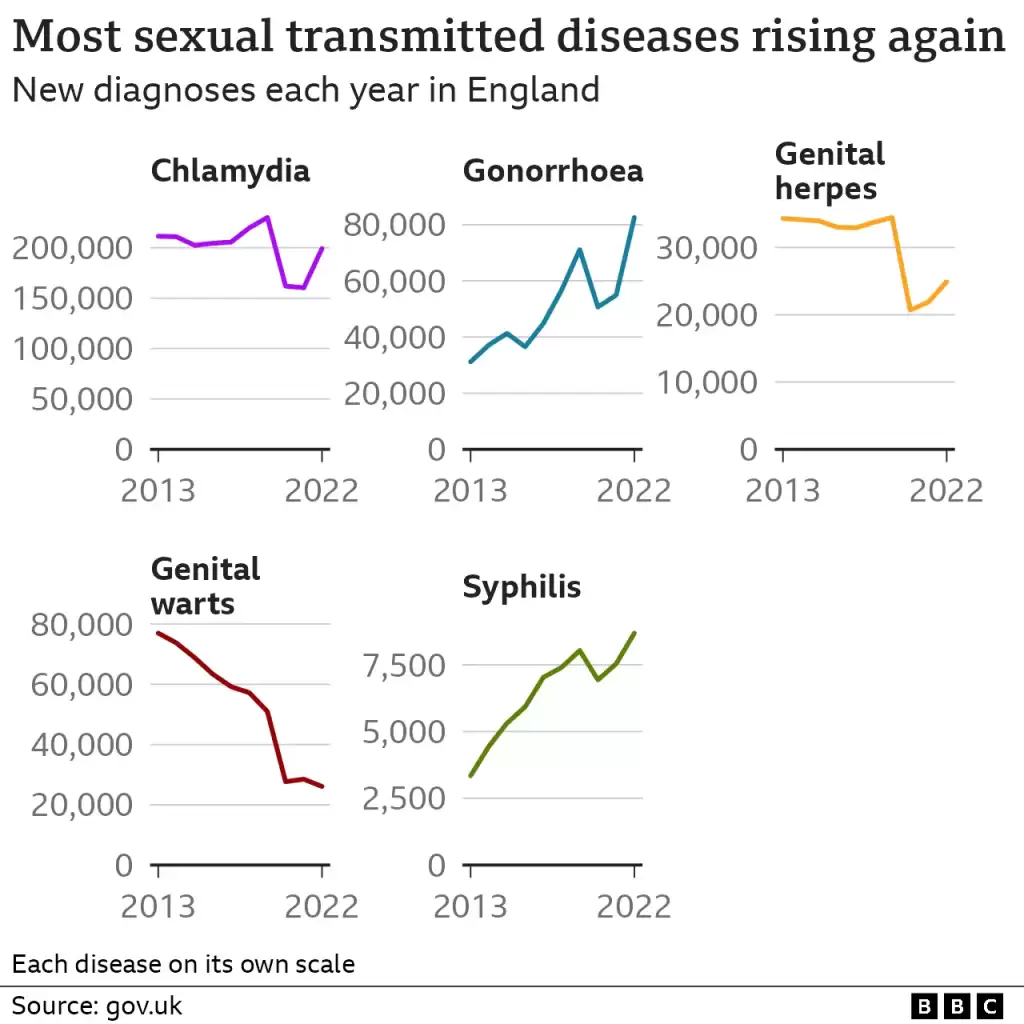
According to bmj.com, “Gonorrhoea diagnoses increased by 50% between 2021 and 2022—from 54 961 to 82 592, the highest number since records began in 1918, the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has warned. Cases of infectious syphilis diagnoses also increased to 8692 in 2022, up 15.2% from 2021 (7543) and the highest number since 1948.”
Currently, people are being urged to practice safe sex to protect themselves and get tested if they may be at risk. Meanwhile, doctors have been told to stay alert given rising records.
Also, data show that people aged 15 to 24 remain the most likely to be diagnosed with an STI, with over 400 diagnoses every day last year among young people.
There were 82,592 cases of gonorrhoea in 2022 – up 50% on the 54,661 recorded the year before, the UK Health Security Agency says.
Syphilis cases increased by 15% from 7,543 to 8,692.
The age group most likely to be diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection (STI) is people who are 15-24.
Some of the rise will be due to increased testing, but the scale of the surge strongly suggests that there are more of the infections around, says the UKHSA.
Condoms are “the best line of defence” it advises.
The figures show:
• There were 2,195,909 sexual health screens or tests carried out – 13% more than in the previous year
• Chlamydia was the most commonly diagnosed STI overall, with 199,233 cases recorded
• Syphilis cases reached the highest in any given year since 1948
• Gonorrhoea numbers were the highest since annual records began in 1918
Dr Hamish Mohammed from the UKHSA said: “STIs aren’t just an inconvenience – they can have a major impact on your health and that of any sexual partners.
“Condoms are the best defence, but if you didn’t use one the last time you had sex with a new or casual partner, get tested to detect any potential infections early and prevent passing them on to others. Testing is important because you may not have any symptoms of an STI.”
Richard Angell, Chief Executive of Terrence Higgins Trust, said cuts to sexual health services were making a bad situation worse: “Sexual health services and public health budgets have been cut to the bone.
“This was exacerbated and laid bare by last year’s mpox outbreak, which left sexual health clinics in the most affected areas unable to provide HIV and STI testing, HIV prevention and access to contraception due to the displacement of these core and vital services. Until sexual health is properly resourced – with an appointment easier to access than a – we won’t see the number of STIs heading in the right direction.”
What is gonorrhoea and how can you get it?
The disease is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
The infection is spread by unprotected vaginal, oral and anal sex.
Symptoms can include a thick green or yellow discharge from sexual organs, pain when urinating and bleeding between periods.
However, vaginal and rectal infections often have no symptoms.
An untreated infection can lead to infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease and can be passed on to a child during pregnancy.
Credits: BBC





